Study Warns Massachusetts Tax Proposal Would Deter Investment, Stifling the “Innovation Economy”
BOSTON – A state constitutional amendment promoted by the Massachusetts Teachers Association and the Service Employees International Union adding a 4 percent surtax to all annual income above $1 million could devastate innovative startups dependent on Boston’s financial services industry for funding, ultimately hampering the region’s recovery from the COVID-19 economic recession, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.
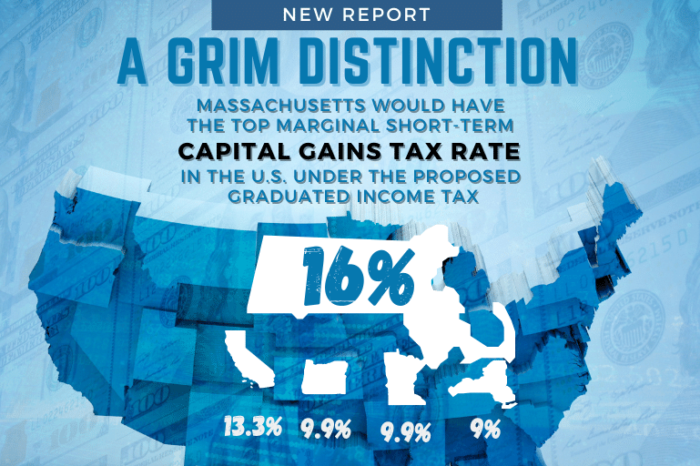
If passed, the surtax would give Massachusetts the highest short-term capital gains tax rate in the nation and the highest long-term capital gains tax rate in New England.
“The particularly punitive aspect of this proposal for investors is that, unlike at the federal level, capital gains can push you into a higher tax bracket under the surtax,” said Greg Sullivan, who co-authored A Grim Distinction: Massachusetts would have top marginal short-term capital gains tax rate in the U.S. under the proposed graduated income tax, with Andrew Mikula. “That could be a significant deterrent to people who would otherwise have invested in small businesses as they emerge from the COVID crisis.”
Research has shown that growth in new “innovation economy” companies exhibits a “multiplier effect” whereby every job created in a high-tech firm supports the creation of up to five more jobs in other sectors of the economy. These other jobs often include low-skill service positions, demonstrating the widespread economic advantages of facilitating private investment in startups. The graduated income tax would provide a powerful disincentive to taxpayers to invest their money in Massachusetts firms.
Pioneer Institute questions the legality of the view held by amendment proponents and the Massachusetts Department of Revenue that the amendment should be interpreted as applying to income from short-term and long-term capital gains. That said, the new study presents an analysis based on DOR’s initial interpretation that the surtax would indeed apply to capital gains.
The new study also demonstrates a correlation between the top marginal tax rate on capital gains and the average value of those gains among millionaires at the state level. Most of the states where average capital gains among the wealthy are the highest have no personal income taxes at all, including Wyoming, Nevada, and Florida. Meanwhile, some of the states with the most prominent financial services sectors in the country, such as New York, California, and New Jersey, have lower capital gains averages and much higher tax rates.
In 2014, the Tax Foundation found that, at 28.1 percent, Massachusetts had a lower combined state and federal capital gains tax rate than the national average of 28.7 percent. However, only California taxes short-term capital gains, such as those from day trading, at a higher rate than Massachusetts.
The graduated income tax proposal would give Massachusetts a short-term capital gains tax rate of 16 percent, far above California’s 13.3 percent. On long-term capital gains, Massachusetts would have a tax rate of 9 percent, higher than that of each of its neighboring states, including New York.
“It’s an obvious point that promoters of the surtax cannot respond to: such sky-high taxes on capital gains will lower the level of investment activity in the state. Why that matters is that over the past several decades, Cambridge, South Boston, and other areas have enjoyed a remarkable economic renaissance driven by innovative firms,” said Pioneer Institute Executive Director Jim Stergios. “Our innovation clusters rely heavily on Boston’s strong investment industry. If we put the investment industry at a disadvantage, we will weaken our innovation clusters, the demand for products and services from industries that do business with our innovation clusters, and ultimately job creation.”
The number of jobs in the financial services sector itself is also significant. In Massachusetts, over 191,000 people worked in either finance or insurance in 2019, and 77 percent of those jobs were in Greater Boston.
About the Authors
Gregory Sullivan is Pioneer’s Research Director. Prior to joining Pioneer, Sullivan served two five-year terms as Inspector General of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and was a 17-year member of the Massachusetts House of Representatives. Greg is a Certified Fraud Investigator, and holds degrees from Harvard College, The Kennedy School of Public Administration, and the Sloan School at MIT.
Andrew Mikula is Economic Research Analyst at Pioneer Institute. Mr. Mikula was previously a Lovett & Ruth Peters Economic Opportunity Fellow at Pioneer Institute and studied economics at Bates College.
Pioneer’s mission is to develop and communicate dynamic ideas that advance prosperity and a vibrant civic life in Massachusetts and beyond. Pioneer’s vision of success is a state and nation where our people can prosper and our society thrive because we enjoy world-class options in education, healthcare, transportation and economic opportunity, and where our government is limited, accountable and transparent. Pioneer values an America where our citizenry is well-educated and willing to test our beliefs based on facts and the free exchange of ideas, and committed to liberty, personal responsibility, and free enterprise.
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research
Related Posts